UNIT 3
States of Consciousness
 Consciousness: our awareness of ourselves and our surroundings
Consciousness: our awareness of ourselves and our surroundings
Daydreams
- they can help prepare us for future events
- they can nourish our social development
- can substitute for impulse behavior
Biological Rhythms
- Annual Cycles: seasonal variations (bears hibernation , seasonal affective disorders)
- 28 Day Cycles: menstrual cycle
- 24 Hour Cycle: our circadian rhythms
- 90 Minute Day: sleep cycle
Circadian Rhythms
- Our 24 hour biological clock
- Our body temperature and awareness changes throughout the day
- It's the best to take a test or study during your circadian peaks
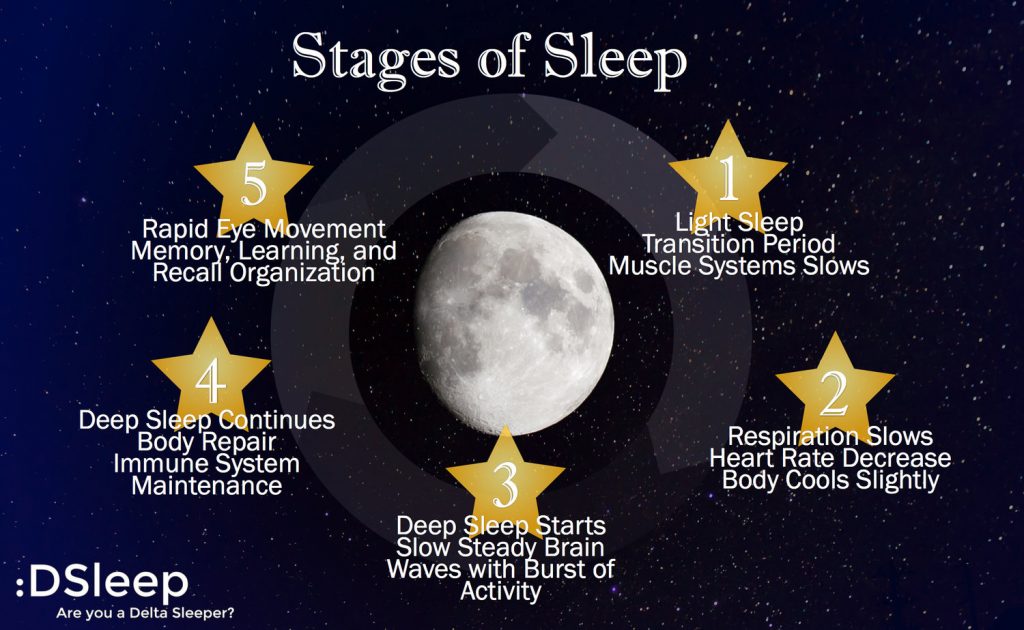
Sleep Stages
- there are 5 identified stages of sleep
- it takes about 90-100 minutes to pass through the 5 stages
- the brainwaves will change according to the sleep stage you're in
- first 4 stages are known as nREM sleep
- the 5th stage is know as REM
- this is experienced as falling to sleep and is a transition stage between wake and sleep
- usually lasts between 1 and 5 minutes and occupies approximately 2-5% of a normal night sleep
- eyes begin to roll slightly
- consists mostly of theta waves (high amplitude, low frequency (slow))
- brief periods of alpha waves, similar to those present while awake
Stage 2
- this follows stage 1 sleep and is the "baseline" of sleep
- this stage is a part of the 90 minute cycles and occupies approximately 45-60% of sleep
- stages 3 and 4 are "delta" sleep or "slow wave" sleep and may last 15-30 minutes
- it's also called "slow wave" sleep because the brain actively slows down dramatically from the "theta" rhythm of stage 2 to a much slower rhythm called "delta"and the height or amplitude of the wave increases dramatically
- contrary to popular belief, it's delta sleep that's the "deepest" stage of sleep (not REM) and the most restorative
- it's delta sleep that a sleep-deprived person's brain craves the first and foremost
- in children, delta sleep can occupy up to 40% of all sleep time and this is what makes children unwakeable or "dead asleep" during most of the night
- REM - Rapid eye movement
- this is a very active stage of sleep
- composes 20-25% of a normal night's sleep
- breathing, heart rate, and brain wave actively quicken
- vivid dreams can occur
- from REM, you go back to stage 2 REM
- body is essentially paralyzed during REM
Sleep Disorders
Insomnia
- recurring problems in falling or staying asleep
- not your once in a while (I have a big test tomorrow) having trouble getting to sleep
- insomnia is not defied by the number of hours you sleep every night
- characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks
- lapses directly into REM sleep (usually during times of stress or joy)
- a sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing during sleep and consequent momentary reawakening
Night Terrors
- a sleep disorder characterized by high arousal and an appearance of being terrified
- occur in stage 4, not REM, and are not often remembered
Sleepwalking (Somnambulism)
- sleepwalking is a sleep disorder effecting an estimated 10% of all humans at least once in their lifetime
- sleepwalking most often occurs during deep non-REM sleep (stage 3 or 4) early in the night
- Manifest Content: the remembered storyline of a dream
- Latent Content: the underlying meaning of a dream
Drugs
Drug Tolerance
- the diminishing effect with regular dose of the same dose
- Drugs are either...
- Antagonists
- Reuptake inhibitors
- if a drug is used often, a tolerance is created for the drug
- thus you need more of the drug to feel the same effect
- if you stop using a drug you can develop withdrawal symptoms
Psychoactive Drugs
- depressants: slows down body functions
- stimulants: arouse body functions
- hallucinogens: distort perceptions or evoke sensations without sensory input
- slows down sympathetic nervous system
- disrupts memory processing
- reduce self-awareness
- involved in up to 60% of all crimes
- the worst drug from a macro-perspective out there
Barbiturates:
- tranquilizers
- taken to sleep (but reduce REM sleep)
- taken with other drugs- you can get a synergistic effect
Opiates:
- has depressive and hallucinogenic qualities
- agonists for endorphins
- morphine, heroin, methadone, and codeine
- all these drugs cross the placental barrier... teratogens
Stimulants:
- speed up body processes
- more powerful ones (like cocaine) give people feelings of invincibility
- amphetamines (speed)
- cocaine
- crack
- "the crash"
Hallucinogens
- LSD (Acid)
- hallucinogens cause distorted perception of the environment
- small amounts change how the brain functions
- brain cells fire at random, causing confusion and distorted perception of reality
I Read About Drug Tolerance And I Didnt Realize That It Only Applies To Street Drugs But It Also Apply To Medicine In Our Own Home. Makes A Lot Of Sense And It Explains Why Allergy Pills Dont Work As Well As It Use To Because I Developed A Tolerance For It.
ReplyDeleteYour notes are very well put together and easy to follow. Just a thought, what is your opinion on addicition. Do you think it is a psychological dependency or a physiological one?
ReplyDeleteGreat job reja! I like how descriptive your blog is and how it clearly identifies every element of every unit you described. it definitely helped me understand the topic much clearly. One thing I want to ask since you've experienced sleep walking. when you woke up was there any sort of hunger or psychological fatigue since you are waking up around your stage 3-4 sleep
ReplyDelete